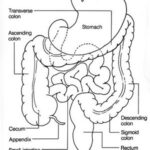
The cause for Crohn’s disease is yet to be found and this poses even a bigger problem for Crohn’s disease in infants. Crohn’s disease in infants causes the lining of the intestine to be inflamed. Usually this occurs in the small intestine or the ileum. However, it can affect the digestive tract in any region, right from the mouth to the anus. The attack of Crohn’s disease may take place once in a few months or a few years and if it continues for many years then the patient’s bowel could possibly get damaged. Crohn’s Disease in infants can increase the chances of the infant, when they are older, in getting cancer by about 20 times. However, Crohn’s disease in infants is not contagious in nature. Though Crohn’s Disease in infants occurs equally in both females and males it has been seen that this disease runs in the family or is more common among certain ethnic groups. As previously noted, there is no real known cause for Crohn’s Disease In Infants, but there are a few theories to explain it. One theory states that the immune system starts reacting in a negative way to bacteria or viruses. Inflammation of Crohn’s Disease in infants is caused by this reaction. The abnormalities of the immune system in patients who have Crohn’s disease, has caused concerns on whether it is a cause for the disease or if it is a result if it.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease in infants can be separate symptoms or a combination of them. Symptoms include pain and cramping of the abdomen, recurring diarrhea that is not related to viral illness or flu, and unexplained high fevers. Other symptoms are anemia, pain in the joints along with redness, and eye inflammation. Some patients have also had abdominal swelling along with pain, sudden and severe constipation, openings or fissures on the skin with no recognizable cause, loss of appetite and rectal bleeding.
In adults Crohn’s disease is known to result in loss of weight and Crohn’s disease in infants causes similar effects, but lack of growth is a more common effect of the disease. Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease in infants is done through blood tests where the doctor checks for anemia or an increased count of white blood cells. Also stool tests show stool cultures that can give evidence of an infection caused by a virus, parasite, or bacteria. In some cases the doctor might use an endoscopy that uses a flexible and small tube with a camera lens and light for a biopsy, which is a tissue sample from the digestive tract that is tested in a laboratory. Doctors have also used barium enema, which is like an x-ray to examine the large intestine and many other types of tests. Crohn’s Disease In Infants still baffles the medical community, but at the same time everything is being done in order to detect it in time and fight it successfully.
Reference
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/info/abdomen/diagnose/crohns.htm
http://www.crohns.net/Miva/education/aboutcrohnskids.shtml